Below we explain the symptoms of a root canal treatment . These are the most common symptoms and if you present them, it is very important that you immediately consult your trusted endodontist.
Only your dentist, through a set of pulpal diagnostic tests, will be able to evaluate and presume the health status of your pulp or dental nerve apply the treatment that you really need.
Without further ado, here is the list and description of endodontic symptoms:

Table of Content
Pain from external stimuli:
An irreversibly inflamed dental pulp can react in a painful way of moderate to high intensity and long duration to external stimuli such as cold, heat or food and drink.
Pain-triggering stimuli:
- Cold can cause a painful reaction if the pulp is inflamed
- The heat in turn can increase the pressure that produces the internal infection of the tooth.
- Food can get into the cavity of the caries and get very close to the pulp, causing pain.
Duration:
In any case, in the face of these stimuli, the pain can last for hours, even after the stimulus has ended.
Intensity:
Pain intensity is moderate to high.
Spontaneous pain
Normally when the dental pulp dies (pulpal necrosis) and there is already an infection inside the tooth or in its surroundings, pain can occur spontaneously, that is, without any type of stimulus that causes it
Pain-triggering stimuli
None; the pain is spontaneous
Duration
The pain is of very long duration
Intensity:
Moderate to high intensity and can be continuous or throbbing pain.
Change in color of the affected tooth
It may be the case that the dental pulp changes its color when it dies, and it can be observed through the superficial tissues of the affected tooth
When this happens, externally you can notice that the tooth no longer has its natural color but has a kind of dark shadow inside.
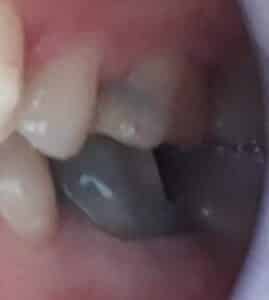
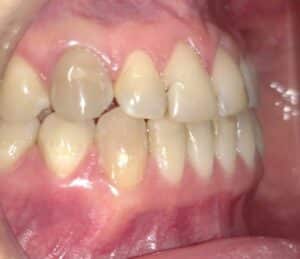
Presence of fistula or abscess, or purulent discharge
When the infection becomes greater, it can leave the interior of the tooth and affect neighboring tissues (bone and ligament).
The defense mechanism of our body then generates pus produced by the bacteria that the immune system manages to kill.
This pus, in turn, forms an accumulation called dental abscess and that, with the Over time it grows and affects both the bone and the neighboring tissues of the tooth.
This growth can be such that the abscess can go through the bone and reach the gum.
In this case you can see a kind of whitish or yellowish ball that sprouts in the gum near the affected tooth and that generates a lot of pain due to the pressure it exerts on the tissues.
This small ball can grow until it explodes and generate purulent secretions.
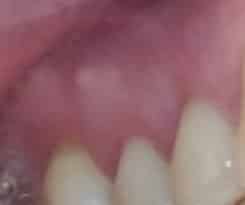
Sensitivity or inflammation of the gums
As a result of the infection and most likely prior to the external appearance of an abscess, sensitivity to touch and inflammation of the gums near the affected tooth may occur.
Most likely an abscess is on the way.
No symptoms
There are times, mainly after pulpal death but before or long after infection, when no symptoms are felt.
This is because the pulp, being dead, no longer has nerve connections and becomes insensitive.
These cases are determined by your dentist mainly after a periapical radiography study
Despite the absence of symptoms, pulpal death will generate them sooner or later, so it must be treated in the same way.
Conclusions
If you present any of these symptoms of root canal treatment, it is very important that you go to the dentist immediately, only he will be able to indicate the correct path to follow in your case.
In the same way, it is vital for us to leave you with the message that it is not necessary for these root canal symptoms to appear, you can very easily avoid reaching this point through adequate prevention.
With simple semi-annual visits to your trusted dentist, you can prevent tooth decay, which is the main cause of endodontic treatments.
The habit of dental prevention is something you should incorporate into your life and that of the people you love.